
Endovenous Laser Ablation
Varicose veins
What is Varicose Vein?
Varicose veins are twisted, enlarged veins. Any superficial vein may become varicosed, but the veins most commonly affected are those in your legs. That’s because standing and walking upright increases the pressure in the veins of your lower body.
Varicose vein Causes
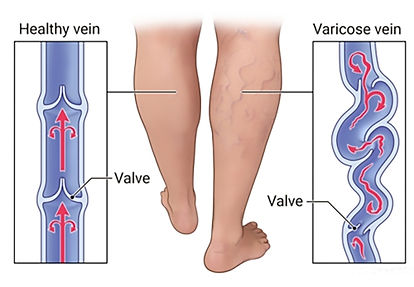
Weak or damaged valves can lead to varicose veins. Arteries carry blood from your heart to the rest of your tissues, and veins return blood from the rest of your body to your heart, so the blood can be recirculated. To return blood to your heart, the veins in your legs must work against gravity.
Muscle contractions in your lower legs act as pumps, and elastic vein walls help blood return to your heart. Tiny valves in your veins open as blood flows toward your heart then close to stop blood from flowing backward. If these valves are weak or damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the vein, causing the veins to stretch or twist.
Types of Varicose Vein
-
Greater saphenous varicose veins
-
Lesser saphenous varicose veins
-
Branch type varicose veins
-
Genital area varicose veins
-
Reticular type or web type (spider veins) varicose veins
Symptoms of Varicose Vein
Varicose veins may not cause any pain. Signs you may have varicose veins include:
-
Veins that are dark purple or blue in color
-
Veins that appear twisted and bulging; they are often like cords on your legs
-
An achy or heavy feeling in your legs particularly in evening time.
-
Burning, throbbing, muscle cramping and swelling in your lower legs
-
Worsened pain after sitting or standing for a long time
-
Itching around one or more of your veins
-
Skin discoloration around a varicose vein
Spider veins are similar to varicose veins, but they’re smaller. Spider veins are found closer to the skin’s surface and are often red or blue.

Call Us For a Friendly
Telephone Assessment
Contact Us
+91 7507200800
Reason for Varicose Vein
-
Heredity
-
Standing in one place for a long time
-
Excessive body weight
-
Changes in hormone level at various stages of life
-
Use of birth controlling precautions
-
Tissue lumps
-
Constipation
-
Injury to the skin
-
Past medical complications

Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
The diagnosis of varicose veins generally starts with a physical examination. After having a glimpse at the affected area, the doctor confirms if those are varicose veins. To confirm the initial diagnosis, the following tests are recommended.
Doppler test :
This test measures the amount of blood flowing through the arteries and veins with the help of high-frequency sound waves.
Color duplex ultrasound scan :
This combines the traditional ultrasound and the doppler test to measure the speed and other aspects of blood flow.

Treatment for Varicose Vein
Endovenous Laser Ablation
Non-operative procedures:
Personal care- daily exercise, use of comfortable clothes, and change the habit of standing or sitting, use of compression stockings to manage blood flow
Subfascial Endoscopic Perforator Surgery: It is a Minimally Access surgery and best alternative to open surgery. The process uses small incisions, and by using the operating scope tied off the affected veins
Sclerotherapy: Useful in the treatment of small and medium-sized varicose veins.
Laser surgeries: Effective in treating smaller varicose veins and spider veins. It holds many advantages over conventional methods. The catheter-assisted process is a type of laser treatment it uses energy in the form of radiofrequency or laser.

Pre-Surgery and Post-Surgery Instructions (Endovenous Laser Ablation)
-
Non-operative procedures:
-
Personal care- daily exercise, use of comfortable clothes, and change the habit of standing or sitting, use of compression stockings to manage blood flow
-
Subfascial Endoscopic Perforator Surgery: It is a Minimally Access surgery and best alternative to open surgery. The process uses small incisions, and by using the operating scope tied off the affected veins
-
Sclerotherapy: Useful in the treatment of small and medium-sized varicose veins.
-
Laser surgeries: Effective in treating smaller varicose veins and spider veins. It holds many advantages over conventional methods. The catheter-assisted process is a type of laser treatment it uses energy in the form of radiofrequency or laser.
Myths of Varicose Vein and spider vein
-
Using high heels daily give rise to varicose veins
-
Varicose veins do not cause any complications
-
Sitting by crossed legs develops varicose veins
-
Varicose veins treatment surgeries are expensive
Treatment for varicose vein: EVLA-Endovenous Laser Ablation
EVLA is a new method of treating varicose veins without surgery. Instead of tying and removing the abnormal veins they are heated by a laser. The heat ablate the walls of the veins and then body naturally absorbs the dead tissue and the abnormal veins are destroyed.
Risk factors
-
Age. The risk of varicose veins increases with age. Aging causes wear and tear on the valves in your veins that help regulate blood flow. Eventually, that wear causes the valves to allow some blood to flow back into your veins where it collects instead of flowing up to your heart.
-
Sex. Women are more likely to develop the condition. Hormonal changes during pregnancy, pre-menstruation or menopause may be a factor because female hormones tend to relax vein walls. Hormone treatments, such as birth control pills, may increase your risk of varicose veins.
-
Pregnancy. During pregnancy, the volume of blood in your body increases. This change supports the growing fetus but also can produce an unfortunate side effect — enlarged veins in your legs. Hormonal changes during pregnancy may also play a role.
-
Family history. If other family members had varicose veins, there’s a greater chance you will too.
-
Obesity. Being overweight puts added pressure on your veins
-
Standing or sitting for long periods of time. Your blood doesn’t flow as well if you’re in the same position for long periods.

Complications of
Varicose vein
-
Ulcers. Painful ulcers may form on the skin near varicose veins, particularly near the ankles. A discolored spot on the skin usually begins before an ulcer forms. See your doctor immediately if you suspect you’ve developed an ulcer.
-
Blood clots. Occasionally, veins deep within the legs become enlarged. In such cases, the affected leg may become painful and swell. Any persistent leg pain or swelling warrants medical attention because it may indicate a blood clot — a condition known medically as thrombophlebitis.
-
Bleeding. Occasionally, veins very close to the skin may burst. This usually causes only minor bleeding. But any bleeding requires medical attention


